FIAT and Federalism
The Issues with FIAT Currency
Dr. Trost mentioned many concerns regarding FIAT currency, primarily the inflationary tendencies of said currencies. With no precious metal backing or hard cap to the amount of currency in circulation, central governments have a high level of control over the economy. As foolish as it sounds, if a government wants to fund something, it can just print more money. This comes at the expense of the average consumer, as the increase in currency supply leads to inflation. Furthermore, this gives the federal government more power to raise revenue for ventures such as warfare without as much input from its citizens. An interesting example of this is the United States Civil War. The union very quickly realized that they lacked sufficient gold reserves to fund their war effort and printed an abundance of “greenbacks” to help fund it.
The Gold Standard
Dr. Trost mentioned two potential solutions to the issues posed by FIAT currency. The first, while not necessarily his first choice, was to return the United States to the gold standard- or some sort of commodity/ precious metal-backed currency. This would, in theory, limit the ability of the Federal government to create currency at will; they would be limited to the amount of gold that they could mine. This, however, has some impracticalities. Foreign nations could insist that payments be made in bullion rather than paper currency. In the modern day of instant exchange, this could present a significant logistical challenge.
Capped Crypto
According to Dr. Trost, the preferred method of capping governmental currency could be some form of cryptocurrency. If the currency didn’t hold any value, it could, at the very least, be capped so that the government could not create additional currency at will. This is very reminiscent of the gold standard from a valuation perspective, but it would help resolve the logistical issues of transporting, exchanging, and liquidating gold bullion. This, however, does pose a substantial risk to the economic prosperity of the nation.
Historical Case Studies
Panic of 1873
With the gold standard as well as any form of capped cryptocurrency, there is a chance of deflation, especially in the transition from a FIAT currency to some other form. The Coinage Act of 1873 effectively established America more firmly on the gold standard by not allowing silver to be exchanged for money at the US Mint and only allowing gold. This had the effect of lowering the amount of available currency, leading to deflationary pressure on the market. This effectively increased the cost of securing capital for investments, as when taking out a loan long term, the money you owed tended to increase in value, which led to the economic growth of the United States dropping by approximately 75% for six years, with unemployment rates skyrocketing. The political fallout from this recession was the Greenback party, which was a party that advocated FIAT currency in the hopes that moderate inflationary policy could be implemented to alleviate the recession.
Panic of 1893
In the depression of the 1890s, a series of government policies resulted in the citizens losing faith in the gold standard, and a run on the United States' gold reserves. This greatly lowered the amount of currency in circulation as dollars were exchanged for gold, and gold, being harder to liquidate, decreased the flow of money throughout the economy. The US dollar was only able to escape complete collapse through the miracle of Crony Capitalism. JP Morgan led a closed-door private deal in which private entities agreed to s private bond sale that replenished the gold reserves of the US government. The resulting economic downturn itself was resolved by the Klondike Gold Rush, which led to moderate inflation of the US dollar. This moderate inflation led to an economic boom in the late 1890s and early 1900s.
FIAT Currency is Good for the Economy?
One thing that I disagree with Dr. Trost is this idea that FIAT currency can be detrimental to economic growth. I understand the ethical concerns of the government potentially funding foreign wars and an increase in centralized power that this brings; however, it is not entirely true that the government can continue to print money with no consequence, at least not with democratically elected leaders. High inflation is political suicide, and wantonly printing money is how hyperinflation occurs. Thus, leaders are greatly incentivized to craft economic policies that benefit their constituents.
Federal Regulations on Commerce
On another note, I appreciated Dr. Trost’s mention of regulation and how the United States inadvertently led to the creation of Deep Seek. This serves to highlight the fact that often the motives of the federal government differ substantially from those of the individual. The federal government sought to ban exporting advanced chips to China when the developments that could come from those chips could have the potential to benefit every American. Rather than leaving that decision up to individual consumers and companies, the American government implemented a policy with ulterior motives that had unintentional far-reaching consequences.
50 Shades of Corruption
Per Dr. Trost’s beliefs about federalism, decentralizing the power of the US Government to all 50 states would hinder corruption and unnecessary governmental regulation. Currently, a company trying to get ahead must sway only a single level of government to gain an upper hand. This is opposed to an entirely federalist system in which 50 separate state legislatures and states could pass laws that were uniquely suited to their interests.
I am concerned that while this lower “corruption” on a national level, we would still see the same sort of “crony-est” policies at a state level that would increase barriers to trade and hamper economic output. While the commerce clause has been utilized to greatly increase the power of the federal government and an exponential increase in bureaucratic regulation since the ratification of the Constitution, this was not its original intent. The idea behind this was that individual states would not impose trade barriers on each other, and to implement this, the power was given to the federal government.
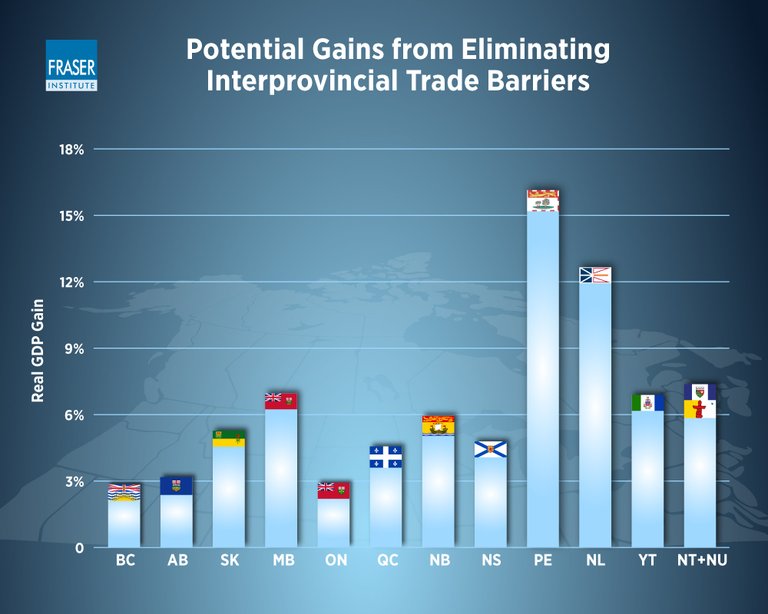
Canadian Case Study
Canada serves as a great example of what happens when this is not the case. The lack of a commerce clause in Canada has led to an increasingly complex network of interprovincial trade barriers. Whether it is the license of the hair stylist not being recognized in one province to another, drastically different requirements for trucks, or actual tariffs placed on goods produced in one province in some instances, Canadian provinces find it easier to trade across the border with the US than with one another.
Congratulations @justaplaneguy! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 20 posts.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP